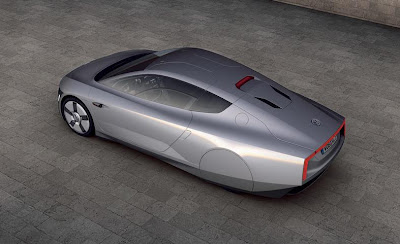
Future mobility is one of the most stimulating topics of our time. The key question here: Just how much could the energy consumption of cars be reduced if all the stops were pulled out for efficiency? There is now an answer to this question, and Volkswagen is delivering it in the form of the new
Volkswagen XL1 Concept. Combined fuel consumption: 0.9 l/100 km. No other hybrid car powered by an electric motor / internal combustion engine combination is more fuel efficient. The prototype makes its world debut at the 2011 Qatar Motor Show (26-29 January, 2011).
2011 Volkswagen XL1 Concept
2011 Volkswagen XL1 Concept
Conceptually, the Volkswagen XL1 represents the third evolutionary stage of Volkswagen's 1-litre car strategy. When the new millennium was ushered in, Prof. Dr. Ferdinand Pi�ch, who is today Chairman of the Supervisory Board of Volkswagen AG, formulated the visionary goal of bringing to the market a production car that was practical for everyday use with a fuel consumption of 1.0 litre per 100 km. In the new XL1, Volkswagen is demonstrating that this goal is now within reach.
2011 Volkswagen XL1 Concept
2011 Volkswagen XL1 Concept
2011 Volkswagen XL1 Concept
2011 Volkswagen XL1 Concept
2011 Volkswagen XL1 Concept
2011 Volkswagen XL1 Concept
2011 Volkswagen XL1 Concept
2011 Volkswagen XL1 Concept
2011 Volkswagen XL1 Concept
2011 Volkswagen XL1 Concept
2011 Volkswagen XL1 Concept
2011 Volkswagen XL1 Concept
2011 Volkswagen XL1 Concept
2011 Volkswagen XL1 Concept
2011 Volkswagen XL1 Concept
2011 Volkswagen XL1 Concept
2011 Volkswagen XL1 Concept
The new Volkswagen XL1 attains a CO2 emissions value of 24 g/km, thanks to a combination of lightweight construction (monocoque and add-on parts made of carbon fibre), very low aerodynamic drag (Cd 0.186) and a plug-in hybrid system - consisting of a two cylinder TDI engine (35 kW/48 PS), E-motor (20 kW/27 PS), 7-speed dualclutch transmission (DSG) and lithium-ion battery. The results: with fuel consumption of 0.9 l/100 km, the new Volkswagen XL1 only emits 24 g/km CO2. Since it is designed as a plug-in hybrid, the XL1 prototype can also be driven for up to 35 kilometres in pure electric mode, i.e. with zero emissions at point of use. The battery can be charged from a conventional household electric outlet. Naturally, battery regeneration is also employed to recover energy while slowing down and store as much of it as possible in the battery for re-use. In this case, the electric motor acts as an electric generator.
Despite the very high levels of efficiency, developers were able to design a body layout that offers greater everyday practicality, incorporating side by side seating rather than the tandem arrangement seen in both the first 1-litre car presented in 2002 and the L1 presented in 2009. In the new Volkswagen XL1, wing doors make it easier to enter and exit the car. Further progress has been made by manufacturing body parts from carbon fibre reinforced polymer parts (CFRP), a technique used in Formula 1 car construction. Once again, Volkswagen has successfully achieved significant reductions in production costs - an important step forward to make viable a limited production run of the XL1. Background: together with suppliers, Volkswagen has developed and patented a new system for CFRP production in what is known as the aRTM process (advanced Resin Transfer Moulding).
Plug-in hybrid concept
With the new XL1, Volkswagen is implementing a plug-in hybrid concept, which utilises the fuel efficient technology of the common rail turbodiesel (TDI) and the dual clutch transmission (DSG). The TDI generates its stated maximum power of 35 kW/48 PS from just 0.8 litre displacement. The entire hybrid unit is housed above the vehicle's driven rear axle. The actual hybrid module with electric motor and clutch is positioned between the TDI and the 7-speed DSG; this module was integrated in the DSG transmission case in place of the usual flywheel. The integrated lithium-ion battery supplies the E-motor with energy. The high voltage energy flow from and to the battery or E-motor is managed by the power electronics, which operates at 220 Volts. The Volkswagen XL1's body electrical system is supplied with the necessary 12 Volts through a DC/DC converter.
Interplay of E-motor and TDI engine: The E-motor supports the TDI in acceleration (boosting), but as described it can also power the XL1 Concept on its own for a distance of up to 35 km. In this mode, the TDI is decoupled from the drivetrain by disengaging a clutch, and it is shut down. Meanwhile, the clutch on the gearbox side remains closed, so the DSG is fully engaged with the electric motor. Important: The driver can choose to drive the Volkswagen XL1 in pure electric mode (provided that the battery is sufficiently charged). As soon as the electric mode button on the instrument panel is pressed, the car is propelled exclusively by electrical power. Restarting of the TDI is a very smooth and comfortable process: In what is known as "pulse starting" of the TDI engine while driving, the electric motor's rotor is sped up and is very quickly coupled to the engine clutch. This accelerates the TDI to the required speed and starts it. The entire process takes place without any jolts, so the driver hardly notices the TDI engine restarting.
When the XL1 is braked, the E-motor operates as a generator that utilises the braking energy to charge the battery (battery regeneration). In certain operating conditions the load shared between the TDI engine and the electric motor can be shifted so that the turbodiesel is operating at its most favourable efficiency level. The gears of the automatically shifting 7-speed DSG are also always selected with the aim of minimising energy usage. The engine controller regulates all energy flow and drive management tasks, taking into account the power demanded at any given moment by the driver. Some of the parameters used to realise the optimum propulsion mode for the given conditions are: accelerator pedal position and engine load, as well as the energy supply and mix of kinetic and electrical energy at any given time.
Two-cylinder TDI uses mass production technology: The 0.8 litre TDI (35 kW/48 PS) was derived from the 1.6 litre TDI, which drives such cars as the Golf and Passat. The 0.8 TDI exhibits the same data as the 1.6-litre TDI common rail engine in terms of cylinder spacing (88 mm), cylinder bore (79.5 mm) and stroke (80.5 mm). In addition, the Volkswagen XL1 Concept's two-cylinder and the mass produced four cylinder share key internal engine features for reducing emissions. They include special piston recesses for multiple injection and individual orientation of the individual injection jets. The excellent, smooth running properties of the common rail engines were transferred to the two cylinder engine. within addition, a balancer shaft that is driven by the crankshaft turning at the same speed optimises smooth engine running.
Meanwhile, the TDI's aluminium crankcase was constructed to achieve high rigidity and precision, which in turn leads to very low friction losses. With the goal of reducing emissions, exhaust gas recirculation and an oxidation catalytic converter as well as a diesel particulate filter are used. Equipped in this way, the 0.8 TDI already fulfils the limits of the Euro-6 emissions standard.
Also designed for efficiency is the vehicle's cooling system. Engine management only cools the TDI by activating an externally driven electric water pump when engine operating conditions require it. This cooling system includes an automatically controlled air intake system at the front of the vehicle to reduce cooling system drag. This thermal management strategy also contributes towards reduced fuel consumption. A second electric water pump, which is also used only as needed, circulates a separate lower temperature coolant loop to cool the starter generator and power electronics.
Running gear with ESP utilises high-tech materials
The running gear is equipped with anti-roll bars at the front and rear and is characterised by lightweight construction with maximum safety. In front, a double wishbone suspension is used, while a semi-trailing link system is employed at the rear. The front and rear suspension are both very compact in construction and offer a high level of driving comfort. The running gear components mount directly to the CFRP monocoque in key areas.
Running gear weight has been reduced by the use of aluminium parts (including suspension components, brake calipers, dampers, steering gear housing), CFRP (anti-roll bars), ceramics (brake discs) magnesium (wheels) and plastics (steering wheel body). Friction-optimised wheel bearings and drive shafts, as well as an entirely new generation of optimised low rolling resistance tyres from MICHELIN (front: 115/80 R 15; rear: 145/55 R 16), contribute to the low energy consumption of the Volkswagen XL1 Concept. Safety gains are realised by an anti-lock braking system (ABS) and electronic stabilisation programme (ESP). That is because sustainability without maximum safety would not really be a step forward. The new VW XL1 shows how these two parameters can be brought into harmony.
Articles Source : Netcarshow